Here's how it would work:
- The tree structure is called a Rectangle Filter Tree.
- For starters, let us consider a data set consisting of a collection of rectangles and show how a data set of rectangles is inserted into a filter tree (just as a data set of strings might be inserted into a binary search tree). Later, we will show how to relate this structure to our original problem of finding intersections amongst rectangles in two data sets.
- The general idea is to break up the region into imaginary sub-rectangles, that are each then subdivided into imaginary (and smaller) sub-rectangles ... and so on. We take our input set of data rectangles and insert each rectangle one by one into the filter tree. The data rectangles are usually quite small and will get inserted into the appropriate sub-rectangle in the tree. Hopefully, if the data rectangles are spread out, then they'll spread out over the tree, allowing for efficient search later on.
- A picture will help us understand the details. Let's
consider inserting the following five data rectangles into
a filter tree that spans the region defined by [(0,100), (100,0)]:
R1 = [(89,57), (91,37)]
R2 = [(12,80), (45,66)]
R3 = [(28,40), (39,29)]
R4 = [(18,70), (32,60)]
R5 = [(79,94), (82,90)]Here are the rectangles depicted in the region [(0,100), (100,0)]:
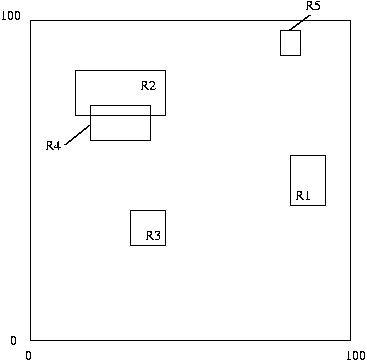
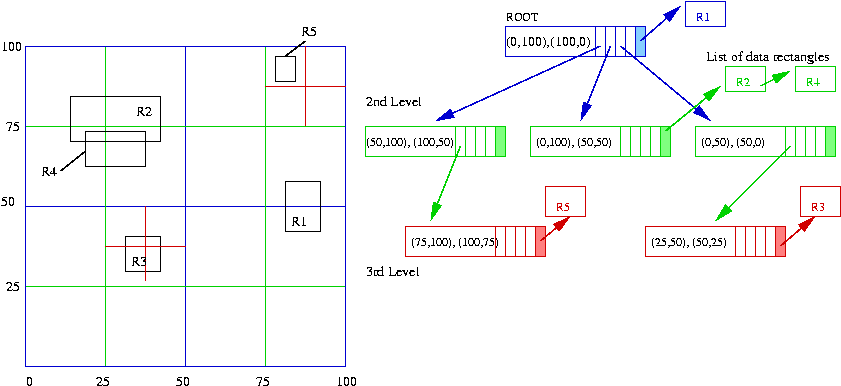
- First, we will look at what the filter tree looks like after
all five data rectangles are inserted. Staring at this might be
enough to understand how it works. We'll go through the steps next.
- Here's an intuitive way to understand filter trees and to see
why it's so named. The enclosing region [(0,100), (100,0)]
represents the root node of the tree. Now the root node has
horizontal and vertical bisectors. The horizontal
bisector is the line that cuts the rectangle in half horizontally;
the vertical bisector cuts the rectangle in half in the vertical direction.
Note that the bisectors together create four smaller sub-rectangles that we will call quadrants (squares, in this particular example). These four sub-rectangles form the four nodes at the next level of the filter tree. Each of these can be bisected horizontally and vertically to form 16 nodes at the third level of the tree ... and so on.
Now suppose we built a wire-frame grid for each rectangle at each level and "dropped" the data rectangles from above. Some data rectangles would fall through the top level (R2, R3, R4, R5), while others (R1) would get "trapped". The level at which a data rectangle gets trapped determines the node in the tree where the data rectangle gets stored. Of course, we limit the number of levels so that eventually a data rectangle gets stored somewhere.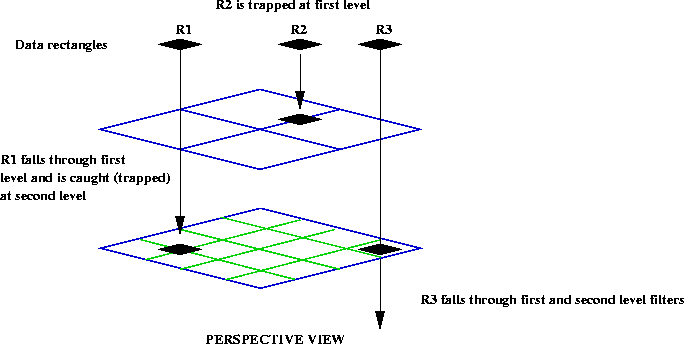
- Now let's examine how the five data rectangles got inserted one
by one.
- In our example, we will build a 3-level tree (Filter trees can have arbitrary depth).
- Initially, the root node is empty and there are no data
rectangles:
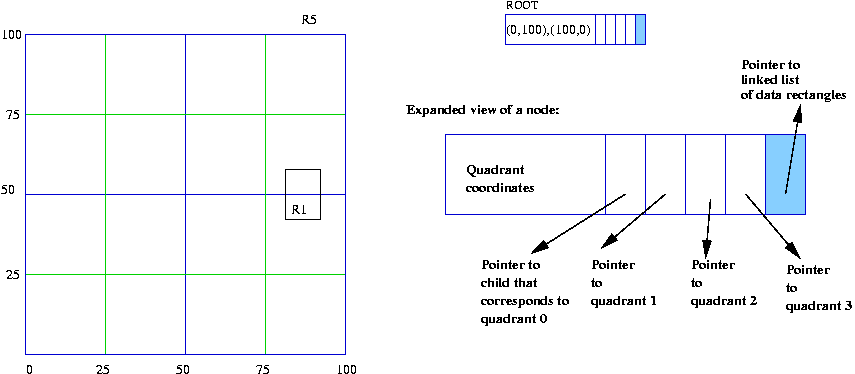
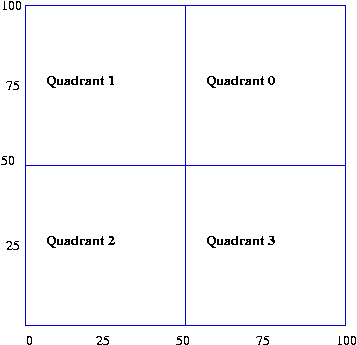
- We will use this convention for numbering the quadrants:
quadrant 0 is the Northeast quadrant, quadrant 1 is the Northwest
quadrant ... and so on.
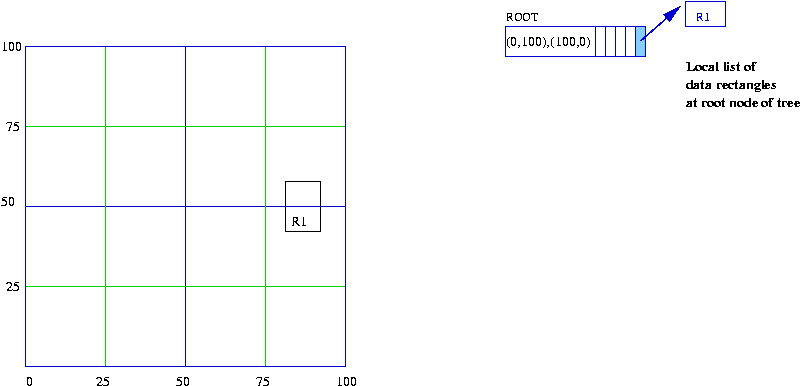
- The first data rectangle (R1 = [(89,57), (91,37)]) is
"dropped" into the current tree. It happens to get trapped at
the root level and is stored in a linked list off of the root level.
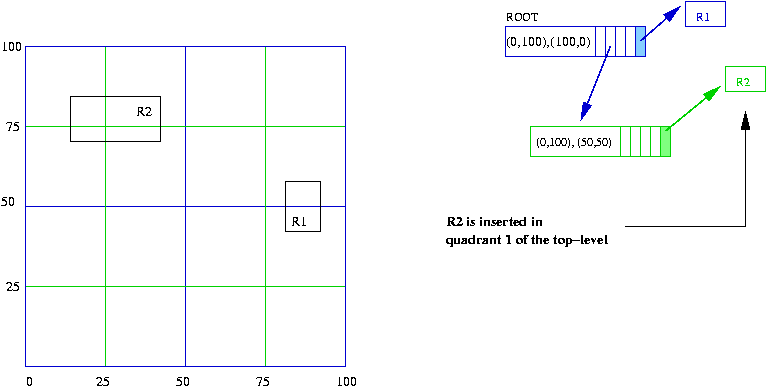
- The second data rectangle (R2 = [(12,80), (45,66)])
is now dropped into the tree. It falls through the root into
quadrant 1. However, no node exists in the tree for quadrant 1,
so we create it. R2 gets trapped by the bisectors of this
sub-rectangle so it gets stored in the linked list off of this
tree node.
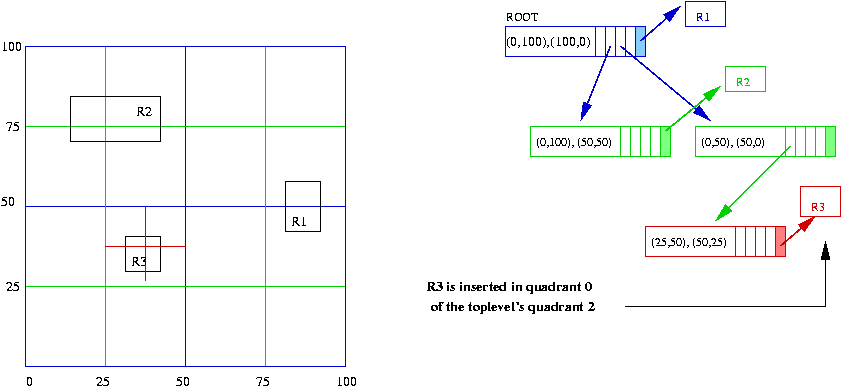
- The third data rectangle (R3 = [(28,40), (39,29)])
is now dropped into the current tree. It falls through the root
node, into quadrant 2, which needs to be created. Once it's
created, R3 also falls through the second-level node into the
third level, where it gets trapped:
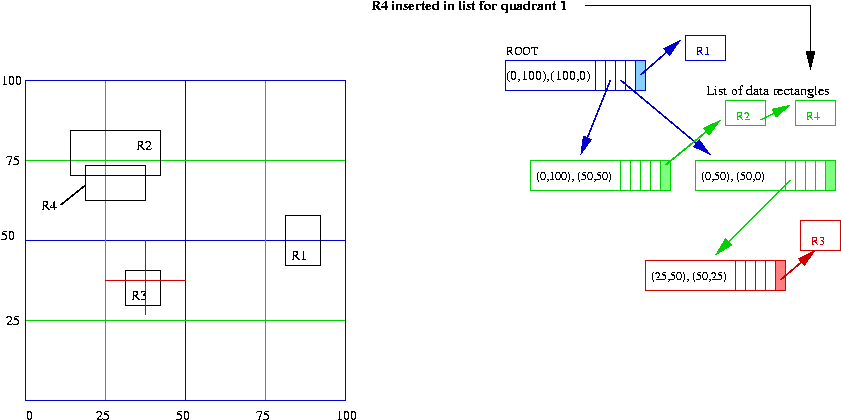
- The fourth data rectangle (R4 = [(18,70), (32,60)]) falls
through the root and gets trapped at the next level in the
rectangle for quadrant 1 (of the root). This is where it gets stored:
- The fifth data rectangle (R5 = [(79,94), (82,90)]) falls
through the root (quadrant 0, which is created), then falls
through quadrant 0 of the second level (which is created
at the third level of the tree). It also falls through the
third level, but since we are limiting the number of levels
to three, we store the rectangle at this level.
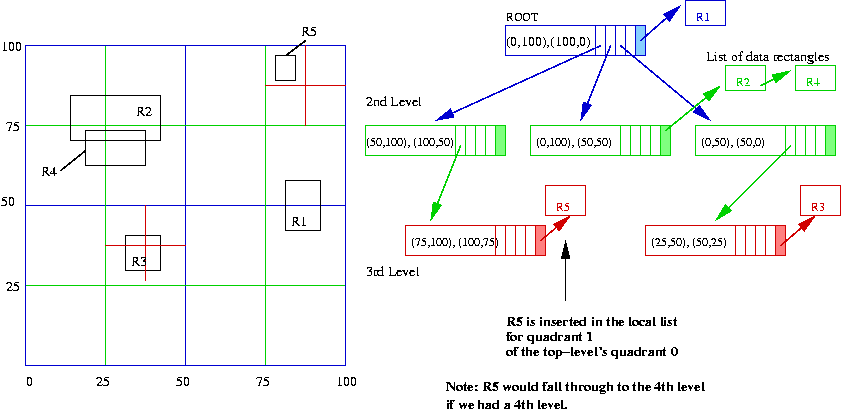
- The tree is now constructed.
- The most important observation to make is that each sub-rectangle in the tree is treated in the same way. Thus, it is easy to write recursive code for insertion.
- Next, consider how searching is done in the tree:
- What does "search" really mean in this geometric-object
context?
=> In search, the input is a "query" rectangle Q for which we need to find all the data rectangles that intersect with Q. - Consider the example Q = [(20,64), (36,38)]. Simply eyeballing the data tells you that Q intersects R3 and R4. But how do we automate searching in the tree?
- The idea is to perform search similar to insertion. Start by checking whether Q intersects any data rectangle stored off of the root node. Then, compute which quadrants Q intersects with. Then recursively search each of these quadrants.
- What does "search" really mean in this geometric-object
context?
- Finally, let's consider how a filter tree can be used for the
two-set intersection problem. Recall that the input to this problem
consists of two sets of rectangles. First, insert one set of data
rectangles into a filter tree. Then, use each rectangle in the
second set to query against the tree.
Algorithm: findIntersections (rectSet1, rectSet2) Input: two sets of rectangles containing n and m rectangles respectively // First, place data rectangles in rectSet1 into tree. 1. makeFilterTree (rectSet1) // Now scan rectangles in second set and query against tree. 2 for i = 0 to m // Get list of intersections from tree. 3. LinkedList intersectionSet = filterTreeSearch (rectSet2[i]); 4. if intersectionSet not empty 5. numIntersections += intersectionSet.size(); 6. Place intersections in intersectionSet into list of intersections; 7. endif 8. endfor 9. return all intersections;
- Name your algorithm FilterTreeRectIntersection.java.
- Your algorithm will need to implement the RectangleSetIntersectionAlgorithm interface that itself extends the Algorithm interface you've already used. Also see the other javadocs referenced above.
- Use instances of the class FilterTreeNode for each tree node. Note that the constructor of this class computes the vertical and horizontal bisectors.
- Note about the region size:
- You can identify the region size by scanning all data rectangles and recording the min and max of the X and Y values.
- However, for the basic test case of showing the same results as in the picture above, you'll need to (just for this test case) use the 100 x 100 region.
- Suggested steps for implementation:
- Start with some pen-and-paper work: write down detailed pseudocode for insertion and search in the filter tree, and for the two-set intersection that uses the tree. Submit this pseudocode in Part I.
- You will find it useful to write code that decides whether two given rectangles intersect. Likewise, you will find it useful to write code to identify whether a given rectangle intersects with a node's bisectors.
- First get your code working for just two rectangles in each rectangle set.
- Implement a print-tree method. Use the 5-rectangle example above to show that your code is working correctly. Submit PDF output from your print-tree with this example, and another example.
- Compare the performance of the filter tree approach with the naive method. Do not spew out debugging into or print-tree output for this part.
- You may use this properties file with the test environment.
- Try filter trees of different depths, and adjust the region and rectangle sizes to see when the filter tree performs well.
- Submit your pseudocode as part of your Part II submission as well.
Submission:
- The written part of Part I is due one week before Part II. However, you would be well-advised to get started with Part II early.
- For this assignment and others, you will need to follow the usual submission instructions carefully.
- For Part I, the name of subdirectory should be: followed by a2part1.
- For Part II, the name of subdirectory should be: your username followed by a2part2.