Database Material
Database Access
- What is a database system>
- Data (database).
- Programs that handle the data (database server).
- Programming language (SQL).
- Typical configuration:
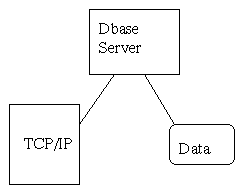
- How it's used by a webserver:
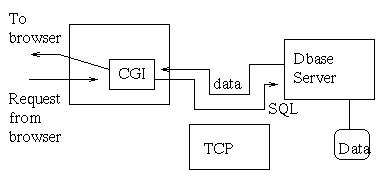
- CGI program realizes dbase needs to be accessed.
- It asks dbase server to get data (using SQL commands).
- Dbase server returns data.
- CGI program formats data in HTML and writes HTML to Browser.
- Several ways in which a CGI program can interface with a
Dbase server:
- Using a custom method used by that particular dbase server.
- Using a standard access method like ODBC/JDBC.
- Rolling the CGI program and dbase client into a single unit.
- Placing the entire webserver inside the dbase server/client.
(e.g., webserver is an Oracle OCI program).
JDBC Access from a Servlet
What is JDBC?
- JDBC = Java DataBase Connectivity.
- JDBC is really a Java class library (java.sql) that
provides a standard way to access databases.
- The idea is that, you can write code using JDBC, and not
worry about the specifics of the database server.
- Today, most database servers come with a JDBC component.
Exercise 11:
Install and test the JDBC driver for mSQL using
these instructions.
Next, let's write a servlet that access a database:
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import java.sql.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class TestJDBCServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
// Set the content type of the response.
resp.setContentType ("text/html");
// Create a PrintWriter to write the response.
java.io.PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (resp.getOutputStream());
// The first part of the response.
out.println ("");
out.println (" Test ");
out.println ("");
// The SQL query.
String sql = "select * from emp";
System.out.println("Executing: " + sql);
// Create a driver instance.
try {
Class.forName("com.imaginary.sql.msql.MsqlDriver").newInstance();
// Make a connection.
String url = "jdbc:msql://localhost:8114/test";
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "simha", "");
if (con == null) {
System.out.println ("Connection unsuccessful");
System.exit(0);
}
else {
System.out.println ("Connection successful. Continuing ...");
}
// Make a statement.
Statement s = con.createStatement();
if (s == null) {
System.out.println ("Statement creation unsuccessful");
System.exit(0);
}
else {
System.out.println ("Statement creation successful ... continuing");
}
// Execute the SQL statement.
if ( s.execute (sql) ) {
ResultSet r = s.getResultSet();
ResultSetMetaData meta = r.getMetaData();
int cols = meta.getColumnCount();
int rownum = 0;
// Iterate over the rows - get one row at a time.
while( r.next() ) {
rownum++;
System.out.println("Row: " + rownum);
for(int i=0; i");
out.println ("");
out.close();
// Screen I/O
System.out.println ("Inside servlet ... servlet complete");
}
public void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
doGet (req, resp);
}
}
For more details regarding JDBC, see the module on JDBC and Native methods.

