Stepwise refinement not only applies to coding, but also to problem-solving.
We'll use an example to illustrate: the maximal rectangle problem
- Given: a 2D binary array (2D array of 0's and 1's).
- Goal: find the largest sub-array (rectangle) consisting
entirely of 1's.
First attempt: the obvious algorithm
- Scan through array, stopping at each element.
- Treat each element as a potential topleft corner of the rectangle.
- For each such topleft corner, try all other elements as a
potential bottom-right corner.
The code:
public class NaiveMaxRect implements MaxRectangleAlgorithm {
// ...
// See if the subrectangle (i,j,a,b) is filled with 1's.
boolean checkFilled (int i, int j, int a, int b)
{
for (int k1=i; k1 <= a; k1++) {
for (int k2=j; k2 <= b; k2++) {
if (A[k1][k2] == 0) {
// Quit as soon as a zero is detected.
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
// Compute the area of rectangle (i,j,a,b)
int computeArea (int i, int j, int a, int b)
{
// Bad input:
if (a < i)
return -1;
if (b < j)
return -1;
// Area.
return (a-i+1) * (b-j+1);
}
// The algorithm.
public int findMaxRectangleArea (int[][] A)
{
// ...
// 1. Initialize.
int maxArea = 0;
// 2. Outer double-for-loop to consider all possible positions
// for topleft corner.
for (int i=0; i < M; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < N; j++) {
// 2.1 With (i,j) as topleft, consider all possible bottom-right corners.
for (int a=i; a < M; a++) {
for (int b=j; b < N; b++) {
// 2.1.2 See if rectangle(i,j,a,b) is filled.
boolean filled = checkFilled (i, j, a, b);
// 2.1.3 If so, compute it's area.
if (filled) {
// Check area.
int area = computeArea (i, j, a, b);
// If the area is largest, adjust maximum and update coordinates.
if (area > maxArea) {
maxArea = area;
topLeftX = i; topLeftY = j;
botRightX = a; botRightY = b;
}
}
}
} // end-3rd-for
} // end-2nd-for
} // end-outermost-for
return maxArea;
}
// ...
}
In pseudocode:
Algorithm: naiveMaxRect (A)
Input: an array with m rows and n columns
1. for i=0 to ... // for each top-left corner
2. for j=0 to ...
3. for a=i to ... // for each bottom right corner
4. for b=j to ...
// Check if rectangle defined by i,j,a,b is filled
5. if checkFilled(i,j,a,b)
6. if larger than largest-so-far
7. record i,j,a,b as largest-so-far
8. endif
9. endif
10. endfor
11. endfor
12. endfor
13. endfor
Some improvements:
- Check area first before scanning for 1's!
⇒ if area is too small, ignore rectangle.
- Eliminate as many size-1 rectangles from search as possible.
- Check corners for 0's before proceeding.
The code:
// ...
public int findMaxRectangleArea (int[][] A)
{
// ...
// 1. Check if array is all zeroes: this is O(mn) work.
boolean found = false;
outer:
for (int i=0; i < M; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < N; j++) {
if (A[i][j] == 1) {
found = true;
topLeftX = botRightX = i;
topLeftY = botRightY = j;
break outer;
}
}
}
// 2. If all zeroes, no further checks are required.
if (! found)
return 0;
// 3. We know there's at least one 1 x 1 rectangle (of area 1).
int maxArea = 1;
// 4. Outer double-for-loop to consider all possible positions
// for topleft corner.
for (int i=0; i < M; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < N; j++) {
// 4.1 With (i,j) as topleft, consider all possible bottom-right corners.
for (int a=i; a < M; a++) {
for (int b=j; b < N; b++) {
// 4.1.1 No need to check size-1 rectangles.
if ( (a == i) && (b == j) )
continue;
// 4.2.1 If a corner is zero, no need to check further.
if ( (A[i][j] == 0) || (A[a][b] == 0) )
continue;
// 4.2.2 First compute area to see if we should scan for 1's.
int area = computeArea (i, j, a, b);
if (area > maxArea) {
// 4.2.2.1 Only if area is larger should we bother checking.
boolean filled = checkFilled (i, j, a, b);
if (filled) {
maxArea = area;
topLeftX = i; topLeftY = j;
botRightX = a; botRightY = b;
}
} // endif-area
} // end-innermost-for
} // end-3rd-for
} // end-2nd-for
} // end-outermost-for
return maxArea;
}
// ...
Analysis (for both variations):
- Suppose the array is m x n.
- Each topleft corner visits about O(mn) locations.
- For each such topleft corner, the bottom right corner visits
no more than O(mn) positions.
- An evaluation (checking for 1's) takes O(mn) in the
worst-case for each rectangle checked.
- Total: O(m3 n3)
(worst-case).
Let's see if we can avoid some unnecessary comparisons:
- Consider this example:
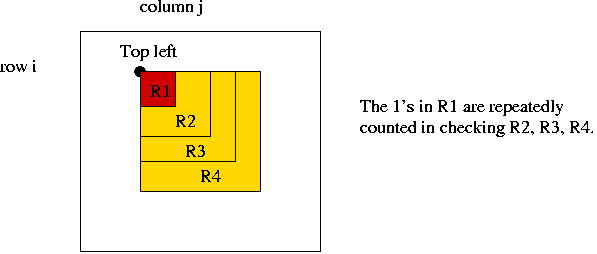
⇒ Small rectangles enclosed by larger ones are always scanned
when processing the larger ones.
- Use bottom up approach:
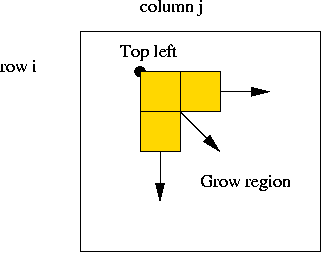
- Start at topleft corner (i, j).
- Grow region rightwards and downwards as much as possible.
- A key observation:
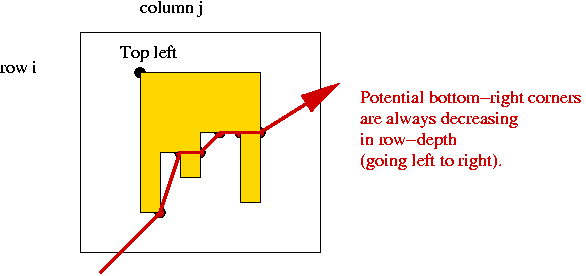
- Consider potential bottom-right corners.
- These form an ascending sequence right to left.
⇒ never need look "deeper" than in previous column.
- Code:
// ...
// Start with top left at i,j and find largest rectangle of 1's.
// Use java.awt.Point to store and return two integers.
Point growRegion (int i, int j)
{
// 1. best_a and best_b will record the best bottom-right corner so far.
int best_a = i, best_b = j;
// 2. a and b will range over possible locations for the bottom-right corner.
int a = i, b = j;
// 3. There is no need to search below rowMax, which is updated
// as we proceed.
int rowMax = M-1;
// 4. Scan left to right along row i using index b as long as there are 1's.
while ( (b <= N-1) && (A[i][b]) != 0) {
// 4.1 Start at the highest possible row, row i.
a = i;
// 4.2 Descend into current column (column b) as far down as possible.
while ( (a <= rowMax) && (A[a][b] == 1) )
a = a + 1;
// 4.3 Back up to the last "1".
a = a - 1;
// 4.4 Update rowMax if we stopped at an earlier row.
if (a < rowMax)
rowMax = a;
// 4.5 Check to see if found a larger rectangle.
int area = computeArea (i, j, a, b);
// 4.6 If the rectangle is larger, update.
if (area > maxArea) {
best_a = a;
best_b = b;
maxArea = area;
topLeftX = i; topLeftY = j;
botRightX = best_a; botRightY = best_b;
}
// 4.7 Continue with next column.
b++;
} // endwhile
// 5. Return best bottom-right corner.
return new Point (best_a, best_b);
}
public int findMaxRectangleArea (int[][] A)
{
// ...
// 1. Check if array is all zeroes.
// ...
// 2. If all zeroes, no further checks are required.
// 3. We know there's at least one 1 x 1 rectangle (of area 1).
maxArea = 1;
// 4. Outer double-for-loop to consider all possible positions
// for topleft corner.
for (int i=0; i < M-1; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < N-1; j++) {
// 4.1 Find the largest possible rectangle with topleft at i,j.
Point p = growRegion (i, j);
// NOTE: growRegion itself updates the current largest rectangle,
// so there's no need to do it here.
}
} // end-outermost-for
// 5. Return value.
return maxArea;
}
// ...
- Have we reduced the complexity?
- Potential topleft corners: O(mn).
- Each execution of growRegion is O(mn), worst-case.
⇒ O(m2 n2) overall.
An improvement:
- As the top-left moves along a row, some columns are repeatedly scanned:
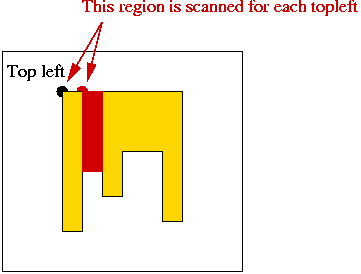
- Idea:
- We only need the number of 1's.
⇒ use a cache.
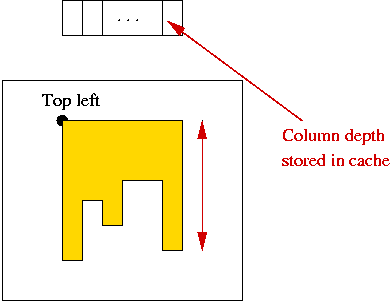
- Pre-compute cache for each row before moving topleft-corner
along row.
- Code:
// ...
// Start with top left at i,j and find largest rectangle of 1's.
Point growRegion (int i, int j)
{
// 1. best_a and best_b will record the best bottom-right corner so far.
int best_a = i, best_b = j;
// 2. a and b will range over possible locations for the bottom-right corner.
int a = i, b = j;
// 3. There is no need to search below rowMax, which is updated
// as we proceed.
int rowMax = M-1;
// 4. Scan left to right along row i using index b as long as there are 1's.
while ( (b <= N-1) && (A[i][b]) != 0) {
// Replace this:
// a = i;
// while ( (a <= rowMax) && (A[a][b] == 1) )
// a = a + 1;
// a = a - 1;
// with:
// 4.1 Descend into current column (column b) as far down as possible - in time O(1)!
a = i + cache[b] - 1;
// 4.2 Update rowMax if we stopped at an earlier row.
if (a < rowMax)
rowMax = a;
else
a = rowMax;
// 4.3 Check to see if found a larger rectangle.
int area = computeArea (i, j, a, b);
// 4.4 If the rectangle is larger, update.
if (area > maxArea) {
// ...
}
// 4.5 Continue with next column.
b++;
} // endwhile
// 5. Return best bottom-right corner.
return new Point (best_a, best_b);
}
// For each row, create the cache that's used repeatedly in the row.
void fillCache (int i)
{
// 1. Initialize, since cache is created just once.
Arrays.fill (cache, 0);
// 2. Walk across the columns.
for (int j=0; j < N; j++) {
// 2.1 For each column position (i.e., potential top-left corner),
// find the longest column of 1's.
for (int a=i; a < M; a++) {
if (A[a][j] == 0)
break;
else
cache[j] ++;
}
} // end-column-scan.
}
public int findMaxRectangleArea (int[][] A)
{
// ...
// Create space for cache - use maximum possible size.
cache = new int [N];
// ...
for (int i=0; i < M-1; i++) {
// Fill cache for row i.
fillCache (i);
// Scan columns in row.
for (int j=0; j < N-1; j++) {
// Find the largest possible rectangle with topleft at i,j.
Point p = growRegion (i, j);
}
} // end-outermost-for
// ...
}
// ...
- Improvement in complexity:
- We have reduced growRegion to O(n) (number of columns).
- Overall: O(m n2).
- However, we require O(n) additional space.
Note: the material on the maximal rectangle problem is based on an
article by D.Vanderwoode in Dr.Dobbs Journal, 1998. Much of the code
is completely re-written here (in Java).
Summary
What did we learn in this module?
- Profiling helps you identify bottlenecks and, therefore,
areas for improvement.
- Pre-stored data is a useful strategy in optimization.
- Some problems (like the rectangle) one, do not fit into
our standard types of algorithm problems.
⇒ Yet, there are opportunities for improvement.
In-Class Exercise 6.2:
Solve the Community Problem.




