

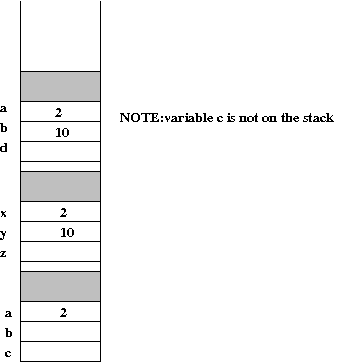

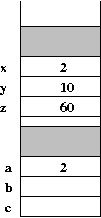

#include <stdio.h>
int ridiculous (int a, int b)
{
static int c = 5;
int d;
/* 3. Before calculation of d */
d = c * (a + b);
/* 4. After calculation */
return d;
}
int silly (int x)
{
int y = 10;
int z;
/* 2. Before the call to ridiculous() */
z = ridiculous (x, y);
/* 5. After the call */
return z;
}
int main ()
{
int a, b, c;
a = 2; /* 1. Before the call to silly() */
b = silly (a);
/* 6. After the call */
c = a + b;
printf ("c=%d\n", c);
}
Exercise 1:
Compile and execute the above program.
Next, consider the six places (1-6, in comments) identified in the execution above. We will draw a (partial) snapshot of the runtime stack at these moments:


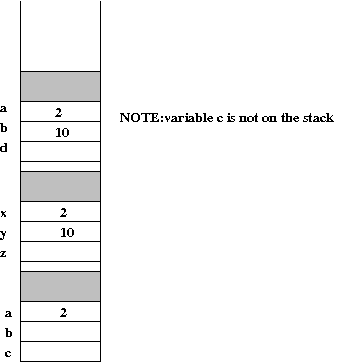

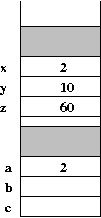

Exercise 2: Examine example2.c and draw detailed snapshots of the stack at various times in the program's execution.