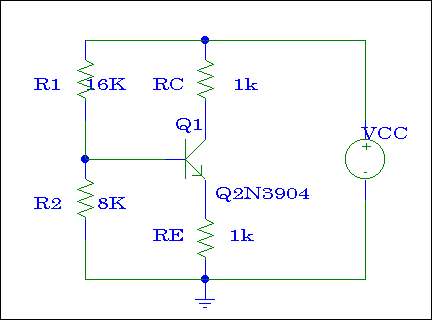
Figure # 1
Bipolar Junction
Transistors
Biasing &
the BJT inverter
Equipment:
You must make up a complete equipment list and have your instructor
review it before you start.
Objectives:

Figure # 1
1.- (HW) DC Biasing Analysis
Using simple Kirchoff's Laws and Ohm's Law, analyze the circuit shown in Figure # 1 and find VE, VC, VB ,VBE, VCE, , IB, IE, IC, RB, (assume VCC = 30 VDC, b = 180, VT = 26 mV). Hint: See the handout - DC Bias for assistance.
Assemble this circuit on ORCAD and perform a bias point detail analysis. Show the calculated voltages and currents by appropriately placing IPROBEs and VIEWPOINTs on your schematic.
Compare the DC Voltages and DC currents obtained from your hand calculation and ORCAD. Why there are some differences?
2.- (HW)
Inverter Simulation
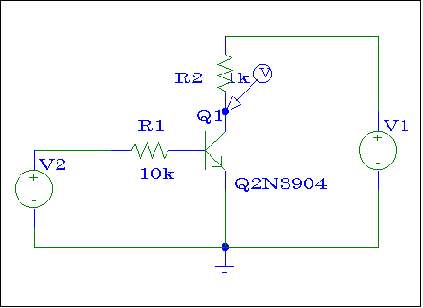
Figure # 2
Use SPICE to simulate the BJT inverter shown in Figure # 2. Plot the
value of the output voltage Vo vs. the input voltage Vi.
Label this plot as "Plot #1 - ORCAD Inverter Simulation".
V1 must remain at 5 VDC while V2 varies from 0 to 5 Volts. Indicate in
the plot when the BJT is in the saturation, linear, or cut-off region.
3.- Verification for DC Biasing and Inverter
4. - Introduction to BJT as an Amplifier
One of the famous BJT application is as an amplifier. There are
three basic configurations and each configuration has a specific application
to electrical circuit. The configurations are:
1) Common Emitter
2) Common Collector
3) Common Base
a) (HW) Using circuit of Figure
#1, derive a formula and find the values for:
i) Voltage Gain of Common Emitter
ii) Voltage Gain of Common Collector
iii) Voltage Gain of Common Base
Hint: To derive the voltage gain for
each configuration, you need to follow these steps:
1) Do a DC Bias Analysis (which you already did in Part 1)
2) Draw a small signal analysis corresponding to each configuration.
For example small signal analysis for
CEC is different from small signal analysis for CCC.
3) Find the expression for Voutput and Vinput.
4) Voltage Gain = Voutput / Vinput.
Check the
textbook : Chapter 4 under BJT as an amplifier for further assistance.
b) By applying a sinusoidal signal (small signal) as the input, measure:
There are several steps that you must do to ensure proper small signal
measurement:
1. Connect a large capacitor between VCC and ground in order
to remove all the noise from the source.
2. Use a really small sinusoidal signal as your input.
Vinput < 100mVp.
3. Check your DC Bias Voltages and Currents before measuring
the small signal. Make sure that the BJT is operating in the
correct Bias Point (DC) before doing any small signal measurement.
4. Use Vpp option in the oscilloscope to measure the Voutput
and Vinput.
4.- Conclusion
1. BJT has been shown to operate as an inverter. Can BJT with a dc power supply (VCC) be used to control appliances that has ac power supply? Elaborate.
2. BJT must stay at one operating point (DC Bias) to operate as an amplifier. Why?