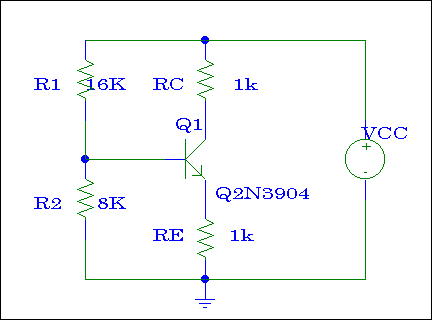
Figure # 1
Bipolar Junction
Transistors
Biasing &
the BJT inverter
Equipment:
You must make up a complete equipment list and have your instructor
review it before you start.
Objectives:

Figure # 1
1.- (HW) Analysis
Analyze the circuit shown in Figure # 1 (use nominal values) and find VBB, VE, VC, VB ,VBE, VCE, , IB, IE, IC, RB, (assume VCC = 30 VDC, b = 180, VT = 26 mV).
Assemble this circuit on SPICE and perform a bias point detail analysis. Show the calculated voltages and currents by appropriately placing IPROBEs and VIEWPOINTs on your schematic.
Repeat part b) but for the value of b equal to 10. Compare your results with those obtained in b).
2.- (HW) Simulation
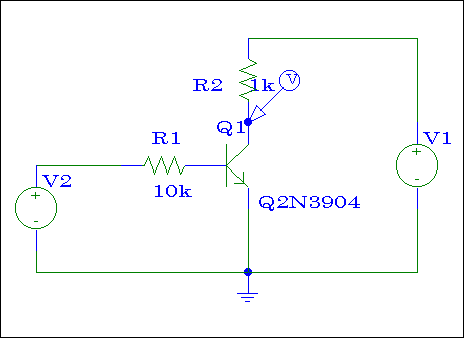
Figure # 2
Use SPICE to simulate the BJT inverter shown in Figure # 2. Plot the
value of the output voltage Vo vs. the input voltage Vi.
V1 must remain at 5 VDC while V2 varies from 0 to 5 Volts. Indicate in
the plot when the BJT is in the saturation, linear, or cut-off region.
3.- Verification
Hand in the output plots for each configuration.
Hint: Connect a large capacitor between VCC and ground in order
to remove all the noise from the source. The noise is amplified and mixes
with the output due to the input AC signal Vs.
4.- Conclusion
Plot the PC-Spice results and the measured results of the BJT inverter
on one plot & compare these results. Write a clear conclusion establishing
the most important facts about the operation of the BJT inverter, the beta
stabilized biasing network and particularly its operation in the different
configurations.