The George Washington University
School of Engineering and Applied Science
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ECE 20 - Fall 2005
Experiment # 5
Bipolar Junction Transistors:
Common Emitter(CE)
Equipment:
You must make up a complete
equipment
list and have your instructor review it before you start.
Objectives:
-
To verify the small signal
performance
for a given CEC amplifier: RIN, ROUT, Av, Ai , maximum input amplitude
without distortion vin max , etc.
-
To design a CEC amplifier
according
to a set of specifications.
-
To establish the relationship
between
the voltage gain and the load.
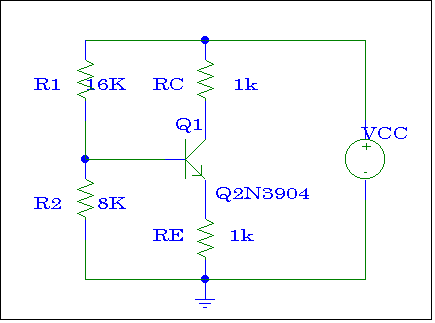
Figure # 1
1.-
(HW)
Analysis
In Exp. #5, the DC Bias Analysis
and general formula for Unloaded Voltage Gain (Avo) for circuit of
Figure
#1 were calculated. The more detailed analysis analysis on Common
Emitter Amplifier for this circuit will be conducted in this section.
When this circuit is operated in
CEC:
-
Find ROUT
-
RIN
-
Unloaded Voltage Gain, Avo
-
Av (RL=ROUT)
-
Ai (RL=ROUT)
-
Maximum input voltage vin max
that the
amplifier can accept before the output distorts (unloaded)
To get a credit for this analysis, you must show all the steps below:
1. Do DC Bias Analysis
2. Draw Small Signal Equivalent circuit for CEC
3. Find Rin, then Rout @Vin=0
4. Find Vout and Vin to get Av
5. Find Av @ RL=Rout
6. Find Ai
7. Find Vinmax
The text book and lab handout should give you a good example on how
to perform the analysis.
2.- Verification
Build and fully test the circuit
shown in Figure #1. By applying a sinusoidal signal such that the small
signal approximation holds, measure:
-
RIN (input impedance) and ROUT
(output
impedance) of the assembled circuit. Read the lab handout to
properly
understand how to measure Rin and Rout.
- Unloaded Voltage gain,
Avo. Label
the plot - "Plot 2a - Avo for CEC"
- Voltage Gain for RL equal to
2*ROUT,
ROUT, ROUT /2, and ROUT /4. Print the output plot for each
case and label each plot as "Plot 2b - Av @ RL= [RL value] for CEC"
- Find the maximum input
voltage that
the amplifier can accept before the output distorts (Unloaded case).
Print
the plot and label it as "Plot 2c - Vin max before output distorts
for
CEC"
- Determine the phase
relationship between
the input and output voltages.
Hint: Connect a large
capacitor
between VCC and ground in order to remove all the noise from the
source.
The noise is amplified and mixes with the output due to the input AC
signal
vs.
3.-
(HW)
Design
Design a Beta-Stabilized
capacitively
coupled Common Emitter voltage amplifier (with shorting capacitor on
Emitter)
similar to the one shown in Fig # 1. Use ORCAD to verify that all the
specifications
have been achieved..
Design Specifications of the
Amplifier
VCC = 24 VDC ± 0.5 VDC
Vsinusoidal = 100
mVpeak
Av = -15
RL = 10 kW
RIN = 5 kW
4.- Assembly, Test and
Verification
of Specifications
Build and test your design.
Measure
and verify that your design meets all the given specifications.
-
Measure VBE, VE, VB, , VCE, IB,
IE,
and IC with no small signal input (Vs).
- Connect the small signal input
and measure
Av, Rin (input impedance) and Rout (output impedance) of the assembled
circuit.
- Find the maximum input voltage
(Vin
max) that the amplifier can accept before the output distorts.
- Measure the phase relationship
between
the input and output voltages.
- Print out the output plot of
Vout and
Vin. Label this plot "Plot 4a - Design of CEC - Vout and
Vin)".
Annotate
in the plot the Voltage gain Av you get from the circuit.
5.- Conclusion
-
Why is there always a big
difference
between the value the function generator was set for and the actual
input
signal?
- Compare the measured results
to your
design calculations and specifications. Explain any differences.
- What can you say about the
general characteristics
of CEC amplifier( Rin, Rout, Av, Ai etc)

